Daemon Process
Systemd
Prerequisites:
- The Artalk binary file, which can be downloaded from GitHub Release
systemctl --version232 or latersudoadministrator privileges
Move Artalk to $PATH, for example:
sudo mv artalk /usr/bin/Test if it works:
artalk versionCreate a user group named artalk:
sudo groupadd --system artalkCreate a user named artalk with a writable home directory:
sudo useradd --system \
--gid artalk \
--create-home \
--home-dir /var/lib/artalk \
--shell /usr/sbin/nologin \
--comment "Artalk server" \
artalkIf you have the Artalk configuration file, ensure that the newly created artalk user has read permissions.
Create the service file:
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/artalk.service[Unit]
Description=Artalk
Documentation=https://artalk.js.org
After=network.target network-online.target
Requires=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=artalk
Group=artalk
ExecStart=/usr/bin/artalk server -w /var/lib/artalk -c /etc/artalk/artalk.yml
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
TimeoutStopSec=5s
LimitNOFILE=1048576
LimitNPROC=512
PrivateTmp=true
ProtectSystem=full
AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_ADMIN CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetCarefully check ExecStart and ExecReload. Ensure that the binary file location and program startup parameters are correct.
For example, change the path of the -c parameter to specify the configuration file and the -w parameter to change the working directory.
Note that all relative paths in the configuration file are based on the working directory. For example, the ./data/ folder in the configuration file, if the startup parameter is -w /var/lib/artalk, will read from the /var/lib/artalk/data/ directory. Ensure the files in this directory are readable and writable by the created artalk account.
After saving the service file, you can set the service to start automatically:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable --now artalkVerify that the service is running correctly:
systemctl status artalkSome common commands:
- Start the service:
systemctl start artalk - Stop the service:
systemctl stop artalk - Check the status:
systemctl status artalk - View logs:
journalctl -u artalk --no-pager | less +G
Tmux
tmux will create a persistent command-line session that remains in the background after SSH or tty disconnection.
Note: tmux sessions will be cleared after the server shuts down or restarts, and you will need to manually rerun the program.
- Create a session
tmux new -s artalk - Run the program
./artalk server
Reconnect to the session: tmux attach -t artalk
View all sessions: tmux ls
Supervisor
Taking Baota Panel as an example: Open the "Software Store," search for and install the "Supervisor Manager":
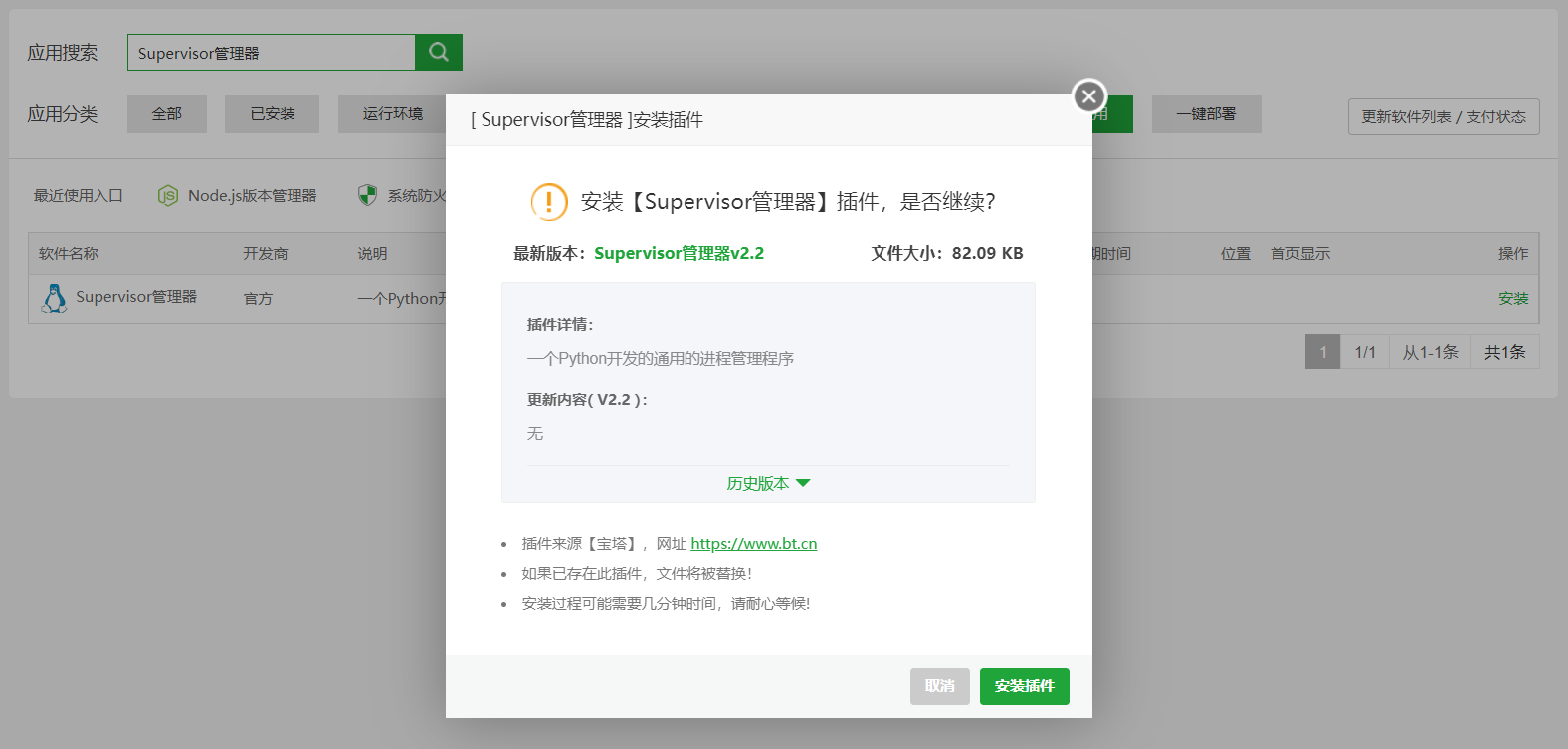
After installation, open the plugin and click "Add Daemon":
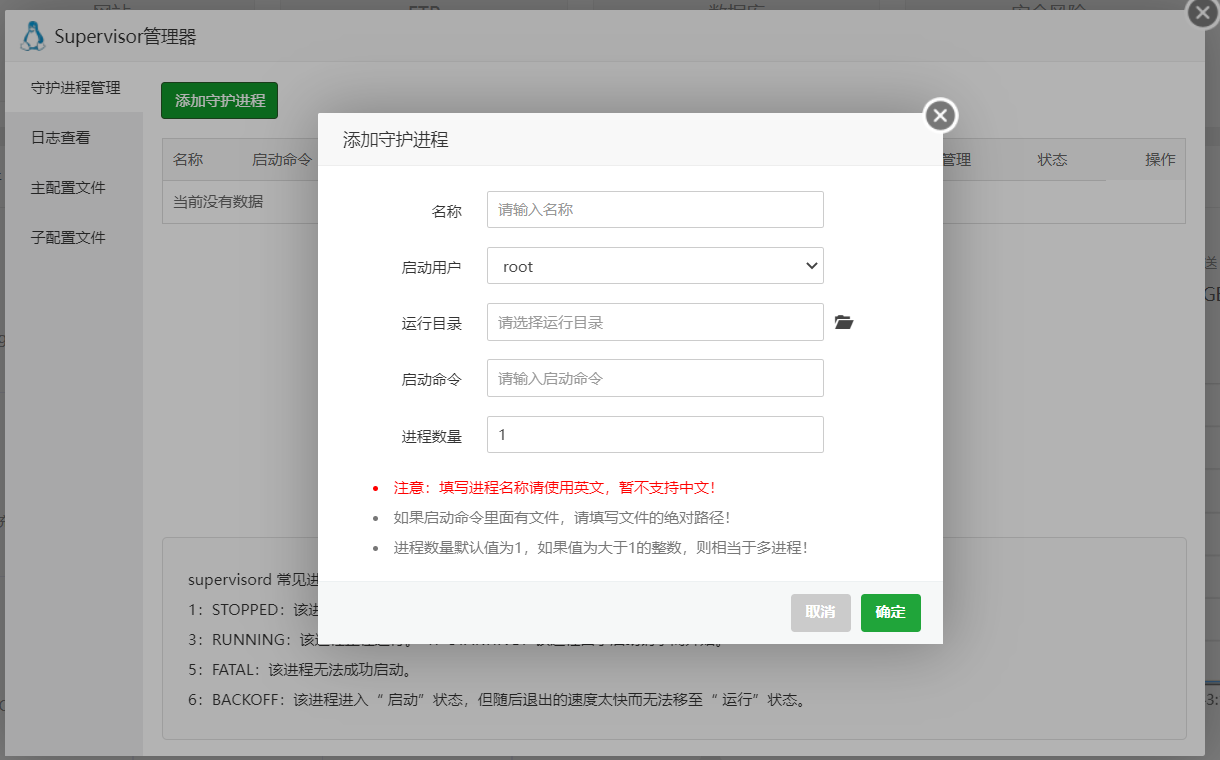
- Startup User:
rootor others- Working Directory: Click the icon on the right and select the Artalk directory
- Startup Command:
./artalk server
Docker
Update the Docker container's Restart Policy to achieve the effect of process daemonization.
docker update --restart=unless-stopped artalkDocker Compose
Add the restart: unless-stopped policy to the service in the docker-compose.yml file:
version: '3'
services:
artalk:
+ restart: unless-stopped qwqcode
qwqcode